Rules of Inheritance (QC)

There are a number of factors that impact QC estate inheritance, including wishes expressed in a will, province law, designated beneficiaries, legal family relationships, and even executor discretion.
Note that if the decedent was a resident of Quebec, the "estate" will officially be known as a "succession".
Before we begin, note also that there are several overlapping terms used to refer to people who inherit from an estate:
- Heir: Someone related to the decedent, who would normally inherit from the estate even without a will.
- Devisee or Legatee: Someone specifically named in the will. Historically, a devisee inherited real estate, and a legatee inherited personal property.
- Beneficiary: General term for someone who will inherit from an estate, but also specifically used for asset classes (such as RRSPs) that bypass probate and go directly to the person named.
To keep things simple, EstateExec uses the common term "heir" when referring to anyone who will inherit from the estate.
Inheritance by Will
If the decedent left a valid QC will, it may grant you a specific item from the estate (known as a bequest), and it may grant you a share of the overall estate.
Bequests
A bequest gives a specific asset or dollar amount to a particular heir (i.e., devisee or legatee).
For example, a will might state that:
- Sally Jones should receive the grand piano
- Tom Smith should receive $10K
Before you can receive the item named in a bequest, the estate must first satisfy any higher priority obligations, such as resolving debts, paying taxes, covering the costs of estate administration, and handling any family entitlements.
An estate must sometimes sell assets in order to be able to meet these obligations, but an executor has a duty to try to avoid selling any items named in a bequest.
Abatement: Regardless, particular bequests can sometimes be only partially honored: perhaps the estate is smaller than expected, or contains fewer items. In such cases, that bequest is said to undergo abatement, and required reductions are typically made proportionately to the recipients. For example, if the estate is worth $100K and there are several cash bequests that total $200K, all bequests would be reduced by 50%. Similarly, if the will bequeaths three pianos to a particular heir, and there are only two pianos in the estate, then the heir would receive just two pianos.
Ademption: Sometimes a particular bequest cannot be honored at all: perhaps the asset is no longer part of the estate; perhaps the bequest conflicts with local law (e.g., community property); or perhaps the asset must be sold (as a last resort) in order to pay estate debts. In such cases, that bequest is said to undergo ademption, and is effectively ignored. For example, if our example estate actually did not contain a grand piano at the time of death, then the bequest of the piano would simply be ignored. There are no "make-up" gestures an executor can do for the intended heir: the executor cannot buy a piano out of estate funds and then honor the bequest, and the executor cannot give the heir additional funds to compensate for the lack of a piano.
Residuary Estate Shares
If you are granted a share of an estate according to the terms of a will, you should receive the specified percentage of the residuary estate: whatever remains after all estate obligations have been met, and any bequests satisfied (to the extent possible).
For example, the will might specify that:
- Susan Smith should receive 25%
- Tina Godfrey should receive 25%
- Jose Martinez should receive 50%
If the gross estate were worth $300K, and had obligations of $100K (perhaps consisting of $50K in credit card debt, $30K in taxes, and $20K in estate administration expenses), the residuary estate would be worth $200K, and distributed according to the above percentages.
- Susan would get $50K
- Tina would get $50K
- Jose would get $100K
If the residuary estate, after resolving all obligations, consisted of a vehicle worth $20K and a bank account containing $180K, the executor could sell the vehicle and distribute the $200K exactly as above.
If it turned out that someone really wanted the vehicle, then it would be best practice for the executor to allocate the vehicle to that heir's share, but the executor is not required to honor such preferences. Similarly, if multiple people wanted the vehicle, the executor could use his or her discretion to decide to sell it, pick a particular recipient, or potentially allocate ownership to multiple recipients. For example, if Susan wanted the vehicle, the executor could distribute the estate as follows:
- Susan gets the vehicle and $30K (total $50K value)
- Tina gets $50K
- Jose gets $100K
Bequests are normally handled before the residuary estate is calculated, so if our example included a $20K bequest to Samuel Iacatelli, then the residuary estate would be worth $180K, not $200K, and the distributions would instead be:
- Samuel gets $20K (the bequest)
- Susan gets the vehicle and $25K (total $45K value)
- Tina gets $45K
- Jose gets $90K
However, people can get creative when writing their wills, and the will might actually specify that a certain heir should receive a particular asset as a part of his or her residuary share.
Intestate Succession
If the decedent left no valid will (i.e., died "intestate"), then inheritance is determined by province law according to legal family relationship (e.g., spouse, child, parent, first cousin, etc.). Different provinces define these intestate inheritance rights differently, but all give significant preference to a surviving spouse and direct children. If no spouse or children survive, then typically the children of the children would inherit. If no direct descendants exist at all, then inheritance typically reverts to the deceased's parents, siblings, grandparents and other next of kin.
If you have been notified that you are entitled to an inheritance due to intestate succession, your inheritance will be equal to the percentage share, as specified by law, of the residuary estate, meaning the estate after all other obligations have been met, such as debts, taxes, and any family entitlements.
For example, if you are entitled to a 10% share of an intestate estate worth $200K after all obligations have been met, you should receive $20K.
Not everything in an estate is cash, however, so your share might include physical items such as a vehicle or a house. Your share might even include partial ownership of something, such as a business, shared with other heirs. An executor may sell assets for various reasons (to pay off debts, or even just to simplify distributions), but is not required to do so. You may express a preference to the executor that your share include certain estate assets, but the executor is not required to honor those wishes.
For example, if an estate included a $20K vehicle, a $5K grand piano, cash equivalents of $200K, and a $500K house, the estate would be worth a total $725K. If estate debts, taxes, and other expenses totaled $125K, the residuary estate would be worth $600K. If you were entitled to 10% of the estate, you would therefore inherit $60K, which could take the from of $60K in cash, or perhaps the vehicle plus $40K in cash. Best practice is for an executor to respect your wishes in terms of the exact contents of your share, but ultimately the executor can allocate share contents as he or she sees fit.
If An Heir Has Died
If an heir died after the decedent, then that heir's estate simply inherits whatever that heir would have inherited.
If an heir died before the decedent, then the following rules generally apply in priority order:
- If the will names an alternate recipient, then the alternate receives the inheritance instead.
- If the recipient was not specifically named, but was instead simply part of a group (i.e., "my children"), then the remaining members of the group split the inheritance among themselves.
- Some wills specifically state that any bequest to a pre-deceased person should instead become part of the residuary estate, and thus be distributed to the residuary heirs along with everything else.
- Otherwise, the particular province's "anti-lapse" laws may apply if the intended heir was a lineal descendant of the decedent (or even just a sibling in some provinces), generally assigning the inheritance to the dead heir's relatives, in a particular priority order (as long as the will does not specifically exclude this). If you are uncertain as to who should inherit in this case, you may want to speak to an estate lawyer.
- If none of the above conditions are met, then the property becomes part of the residuary estate, and is distributed to the residuary heirs along with everything else.
- If there are no surviving residuary heirs, and the province's anti-lapse statute did not apply (perhaps because there were no qualified blood relatives of the deceased residuary heirs), then the residuary estate is distributed according to the province's laws of intestate succession (as if there were no will).
QC Family Entitlements
Regardless of whether there is a will or not, many provinces have laws designed to protect a surviving spouse and dependents, ensuring that they receive at least a minimal amount from the estate as they try to put their lives together and move on. These entitlements usually have precedence over debt claims (other than funeral and estate administration expenses), and even distribution wishes expressed in a will, or intestate succession calculations.
Typical entitlements include personal property exemptions, a homestead, and a family living allowance. Many provinces also provide for a surviving spouse elective share, which allows a spouse to disregard the will and instead claim a share of the estate as mandated by law. In contrast to other family entitlements, a spousal elective share is normally calculated after all debts (and any other obligations) have been resolved.
Quebec allows a surviving spouse and dependants to claim certain entitlements; only once these potential entitlements are dealt with can the normal succession process proceed:
Family Home
A surviving spouse or other dependant has the right to continue living in the family home for 6 months after the death.
Family Patrimony
Before settling the rest of the succession, a liquidator must first allocate half the net value of the family patrimony to any surviving spouse.
Patrimonial assets include all the property used by your family, regardless of whether it is owned by you or your spouse, such as:
- Residences used by your family (e.g., condominium, house, cottage)
- Furniture and other items used by the family in those residences (e.g., bed, TV, stove, table)
- Motor vehicles used for family transportation
Patrimonial assets exclude:
- Personal property that only you or your spouse use, such as jewelry
- Gifts or bequests (and any subsequent increases in value) to one of the spouses either before or during the marriage or civil union
- A business or farm, except the residential portion
- Cash and bank accounts
- Savings bonds, treasury bonds, shares and other investments (except RRSPs)
- Amounts accrued by in a profit-sharing plan, supplementary pension plan for high-income earners, or a non-registered annuity plan
See Civil Code of Québec, CQLR c CCQ-1991, s 414-430.
Marital Regime and Acquests
After partitioning the value of any family patrimony, the liquidator must next settle the liquidation of any matrimonial or civil union regime.
If there is a marital or civil union contract, partition the assets accordingly.
If there is not such a contract, then the partnership of acquests regime applies, which basically says that a surviving spouse is entitled to half the acquests made during the marriage or civil union. The acquests of each spouse include all property not declared to be private property by law, and, in particular, the proceeds of that spouse’s work during the regime, and the fruits and income due or collected from all that spouse’s private property or acquests during the regime.
The following types of property are considered private, and not acquests:
- Property owned or possessed by a spouse when the regime comes into effect
- Gifts or bequests (and any subsequent increases in value) received by a spouse during the regime, if the testator or donor has so provided
- Property acquired by a spouse to replace private property and any insurance indemnity relating thereto
- Rights or benefits of a spouse as a subrogated holder or as a specified beneficiary under a contract or plan of retirement, other annuity or insurance of persons
- A spouse’s clothing and personal papers, wedding ring, and decorations
- Instruments required for a spouse’s occupation
See Civil Code of Québec, CQLR c CCQ-1991, s 448-491.
Family Support
A surviving spouse or other dependent may claim a financial contribution from the succession as support, the amount of which cannot exceed the difference between 1/2 of the share he or she could have claimed had the entire succession, including the value of any gifts during the preceding 3 years, devolved according to law, and what he receives from the succession. Any such claim must be made within 6 months after the death. See Civil Code of Québec, CQLR c CCQ-1991, s 684-695.
Automatic Transfers
While other provinces support automatic transfer of property via named beneficiaries for RRSP accounts, and via right of survivorship for jointly owned real estate, Quebec supports neither of these types of transfers. In Quebec, basically all property must be transferred via succession.
Additional Information
For more information about inheritances in general, see EstateExec Heir Guide.
In case you're interested, inheritance rules in other provinces can be found here:
Estate Obligations & Insolvency
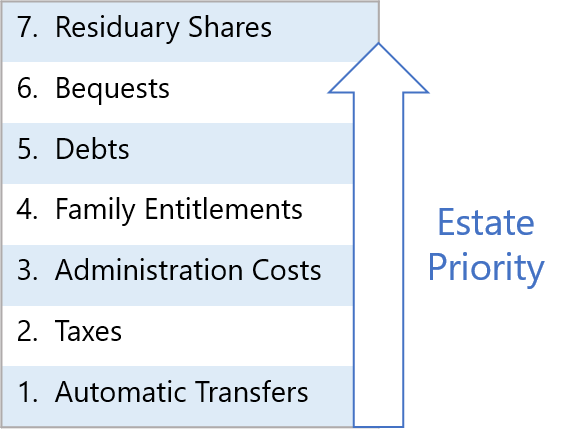
As mentioned in the preceding sections, an estate must allocate its resources in a defined priority order. Certain transfers (such as to RRSP beneficiaries) happen automatically outside the control of the estate, and the estate itself must then ensure it has enough funds to pay all taxes, then estate administration costs, then any family entitlements, then any general debts, and with anything left over, fulfill any will bequests, and finally distribute the residuary estate.
Province law determines which debts have priority over other debts, and some debts (such as funeral expenses) often have priority over family entitlements, but these specifics are the responsibility of the estate executor, and really only matter if the estate cannot pay all its bills.
If the estate runs out of money paying one tier, then subsequent tiers are left with nothing. Consequently, even if you have been bequeathed an item, or are entitled to a residuary share of an estate, you may end up with less than expected. If the estate cannot pay all its debts, the estate will be considered insolvent. If the estate turns out to be insolvent, you will not receive anything at all ... but neither will you be responsible for the remaining debts. However, some provinces do allow creditors to pursue recipients of automated transfers if the estate cannot pay their claims, so if you received an automated transfer, it is possible you would have to pay some or all of it to an estate creditor (this is rare).
EstateExec™ Leaves More $ for Heirs!
EstateExec will likely save the estate thousands of dollars (in reduced legal and accounting expenses, plus relevant money-saving coupons), leaving more funds for distributions to heirs.
- Awarded Best Estate Executor Software in North America at the Worldwide Finance Awards
- Named Best Estate Executor Tool – – by Retirement Living
- Web Application of the Year Winner at the Globee Business Excellence Awards 2022
- Winner of Best Executor Software at the Software and Technology Awards
- Rated 4.9 stars – – on TrustPilot reviews