Manage Distributions
Show Table of ContentsUltimately, an executor must distribute the estate's net assets to the heirs (see Guide: Making Distributions for an explanation of the overall distribution planning and execution process).
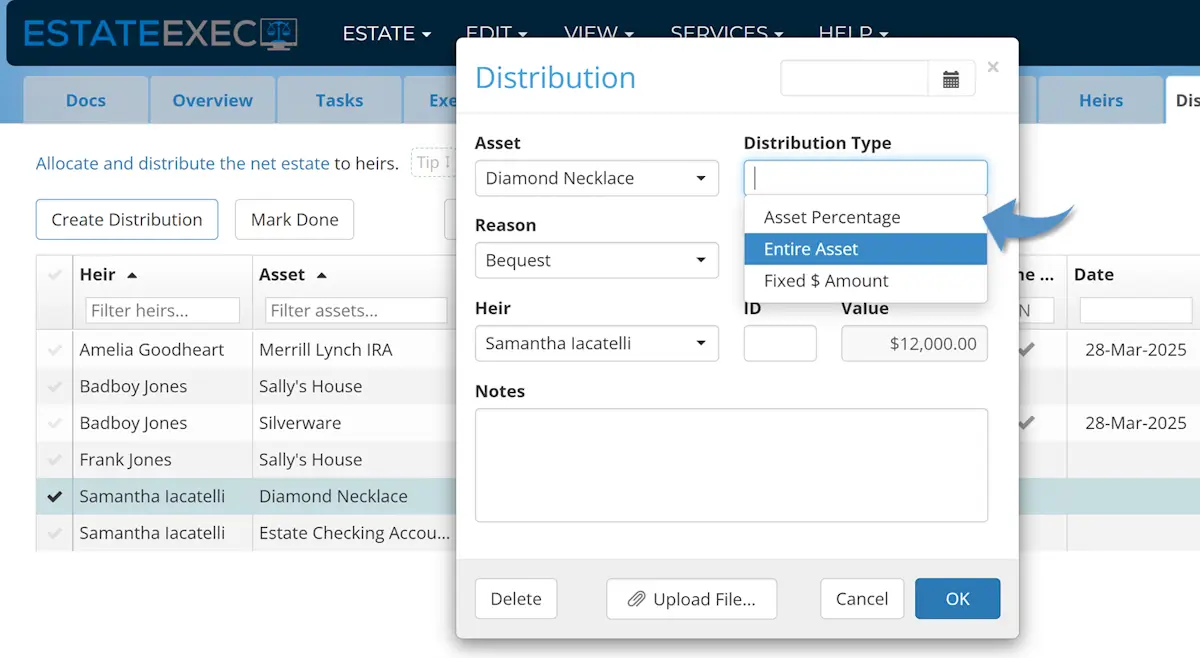
Create Distribution
Within EstateExec, a distribution represents the assignment of an asset (or portion of an asset) to a given heir.
You can define a distribution any of the following ways:
- By clicking the Distributed cell of an asset on the Assets tab
- By clicking the Create Distribution button on the Distributions tab
- By clicking the Create Transaction button on the Cashflow tab, then selecting Distribution for the Category in the Transaction dialog that appears
Use whichever method is easiest for you (they all accomplish the same thing), and note that before creating a distribution, you must first have defined one or more heirs, and one or more assets.
Date
The date (in the top right of the dialog) represents the date an asset was actually delivered to the heir. If you are just in the planning phase, it can be very helpful to define distributions in advance, allocating but not actually yet delivering estate assets. To indicate that you are just planning a distribution, and have not actually made it, clear the date field and leave it blank.
Asset
The distribution asset can be any asset defined on the Assets Tab (e.g., a diamond necklace, a house, cash being distributed from a bank account), and in the next field you can define whether you are distributing the entire asset or just a portion to a given heir.
- If some of the assets in the dropdown Asset selection list are grayed out, that means those assets have already been settled (e.g., completely distributed, sold, transferred, etc.) and are thus unavailable for new distributions.
- If the entire Asset field is grayed out, with an asset pre-selected, that's because you started the distribution on the Assets Tab by clicking a given asset's Distributed cell (i.e., you have already chosen the asset, so no need to do so again).
Distribution Type
You can define the type of distribution in one of 3 ways:
- Asset Percentage: You wish to give an heir a defined percentage of an asset (e.g., 50% of the house).
- Entire Asset: You want to give 100% of an asset to a given heir (e.g., a diamond necklace).
- Fixed $ Amount: You want to give an heir a specific dollar amount (e.g., a $5,000.00 bequest).
If the will specifies a certain percentage, it's best to express the distribution that way. When specifying a distribution by percent, you can override the calculated value if you need to tweak it. For example, if the will divides things equally among 3 heirs, you can specify in each distribution that the heir gets 33.333%, and override the Value field in each distribution as necessary so that they are all exactly equal and the asset has no remaining value. If you like, you can set one of the heirs to get 33.334%, so the combined amount is exactly 100%, and simply ensure that the values of each distribution are set to the proper identical amount.
Note: By its nature, a percentage distribution is proportional to the corresponding asset's value. If you define a percentage distribution, and then later adjust the Value Now of the asset, the distribution will adjust to reflect the specified percentage of the new value. Once you assign a date to a distribution, though, its value becomes fixed, and any subsequent changes to the asset's Value Now will not affect the distribution (which you presumably already made in the real world). Because of the dynamic nature of future percentage distributions, you cannot override the value of such a distribution until you assign a date, signalling that you have actually made the distribution.
Some other notes about partial distributions:
- To see all distributions associated with an asset, either filter the Asset column in the Assets table, or click on the asset's Distributed cell in the Assets table.
- An asset's "Distributed" cell in the Assets table will be shown in gray if any of its distributions are not yet done, and the asset's "Value Now" will reflect the remaining undistributed amount. Only the amount actually distributed will be included in the "Distributed" column sum at the bottom of the table.
- A subtle but important point is that if the asset's value and/or cost base fluctuates during the time between one partial distribution and another, the same percentage of the asset may end up being recorded as different distribution values. This is correct, but can cause complications in the real world, so it's best to distribute all portions of an asset simultaneously. Once you set a distribution's date, changes to its asset's remaining Value Now or Adjusted Cost Base will only affect remaining partial distributions that have not yet been made.
- If you define fixed $ amount distributions and percentage distributions from the same asset, and haven't yet assigned dates to those distributions, EstateExec will assume you intend to distribute all the fixed $ amount distributions before distributing the defined percentages of whatever is left over.
Reason
The reason for the particular distribution may have tax and other distribution implications:
- Automatic - A distribution controlled outside the will (such as an RRSP with a named beneficiary)
- Bequest - A distribution specified by the will
- Residuary - A distribution of the residuary estate
Heir
The available list of heirs comes from your entries on the Heirs tab (EstateExec uses the term "heir" to mean anyone who will inherit from the estate). If an asset will be split among multiple heirs, create one distribution per person, setting the Distribution Type for each distribution to either Asset Percentage or Fixed $ Amount (Asset Percentage is usually best, so that if the asset fluctuates in value, you won't have to keep editing the distributions to tweak them).
If you select the decedent's spouse (as specified on the Heirs tab), an additional checkbox will appear so you can defer any deemed proceeds that would have otherwise been associated with the portion of the asset handled by this distribution. By default, this box is checked, and once you save the transaction, EstateExec will automatically adjust the asset's deemed proceeds, ACB, and other dependencies.
If the asset is a Retirement Account (e.g., RRSP), you will instead be shown a checkbox allowing you to indicate that this distribution should be considered a spousal rollover, and thus the ACB at Death should be set to $0 rather than automatically stepped-up to market value (note that if you do this, you will need to notify the CRA of the rollover so it can adjust the decedent's T4 slip).
If you have already adjusted an asset's ACB at Death via the Assets table or the Edit | Asset Cost Base menu, you will be shown a second checkbox which you can use to tell EstateExec not to further adjust the asset's ACB at Death due to this distribution.
Residuary Estate Percentages
It's common to have to distribute a certain percentage of the residuary estate to a given heir. This is easy enough if the estate is simply a pool of cash, but gets a little more challenging when there are assets that will not be liquidated before distribution.
Note that if an heir is entitled to receive 15% of an estate, that does NOT mean that the heir needs to receive 15% of every asset. It just means that total value of whatever the heir receives from the residuary estate must equal to 15% of the value of the residuary estate, and as the executor, you get to decide (for the most part) how to mix and match assets to make things work.
To help monitor and achieve distribution percentage goals:
- Enter target distribution percentages for any relevant heir on the Heirs tab.
- Create distribution allocations as desired (as described above).
- Check the Heir Target Allocation chart on the Overview tab, or the Estimated $ vs Allocated $ columns on the Heirs tab to see how well you are meeting the targets.
- Adjust the distributions accordingly. Note that some assets might need to be split among heirs, and others might need to be liquidated in order to make everything work out.
You can also see everything you've allocated for a particular heir by going to the Distributions tab and filtering the Heir column by the desired name. You can see how much you've actually distributed to that heir by further filtering the "Done" column with "Y" (for "Yes").
Charitable Donations
A charitable donation is really just an estate distribution to a special type of heir (a charity). To record a charitable donation:
- Create a new heir which is the charity.
- Create a distribution in the normal way, as explained above.
Impact on Asset Value and Adjusted Cost Base (ACB)
An asset's Value Now will be unaffected by a distribution until the distribution is assigned a date (the date indicates the distribution has actually been made).
Once an asset has been distributed (or settled in some other way), the asset's "Value Now" in the Asset table becomes blank since the asset is no longer in the estate.
If an asset has only been partially distributed (e.g., 40%), only the percentage of the those distributions are removed, and so there may be some remaining asset "Value Now" until the rest of the asset is distributed.
All of the above applies to an asset's ACB as well, with the exception that a spousal distribution (marked as a spousal rollover, or deemed proceeds deferral) will immediately affect the asset's ACB even if not yet marked done. This is because deemed proceeds must be calculated early in the settlement process, before distributions can legally be made. See Manage ACB for information on tracking ACB using EstateExec.
Using Tables
You can do some very helpful things with EstateExec tables. For example,
- To see everything you have allocated to a given heir, simply go to the Distributions tab and type that heir's name in the filter cell for the Heir column.
- To see all the assets you have not yet allocated, simply go to the Assets tab and type a small value (e.g., 1) in the filter cell for the Distributed column, and a small value (e.g., 1) in the filter cell for the Value Now column.
- Note that when some portion of asset has been allocated but not yet actually distributed (i.e., no date has been entered for the distribution), the Assets table Distributions column shows the total allocated amount for the asset in gray, and the total at the bottom of the column includes only the amount actually distributed in black.